|
*64. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
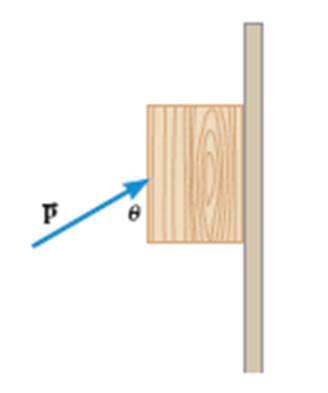
Consider two free body
diagrams, one for the block going up wall and one for the block sliding down
the wall. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
For block going up wall sum of
force equations are |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Since block is not accelerating
horizontally |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
With the angle defined as it
is in the picture, the horizontal or x component is opposite of the angle and
therefore goes with Sin instead of the usual Cos |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Since we are told the block is traveling up the wall with constant
speed. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
For block going down wall sum
of force equations are |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Since block is not
accelerating horizontally No real change |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Since we are told the block is traveling up the wall with constant
speed. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|