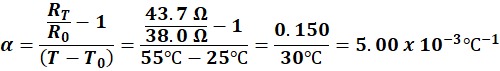|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
13. A coil of wire has a resistance of 38.0 Ω at 25 °C and 43.7 Ω
at 55 °C. What is the temperature
coefficient of resistivity? |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Resistance with temperature
dependence is found from using temperature
dependence of the resistivity. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Usually the reference
temperature is 20 °C,
ρ0 is the
resistivity at 20 °C,
but it can be any temperature you know the resistivity at. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Again, we need to know what
the resistance R0 is at the reference temperature T0. Here we can use the 25 °C as our reference temperature. Since we know RT, R0,
T, and T0 we can solve for a |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|