|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
P 5.5-12 Use Nortonís
theorem to formulate a general expression for the current i in terms of the variable
resistance R shown in Figure P
5.5-12. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Answer: i = 20/(8 + R) A |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Figure
P 5.5-12 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Find the Norton equivalent
circuit to everything except resistor R.†
First deactivate the voltage source and find the equivalent resistance
between points a and b. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Rearrange this to make
identifying the resistor relationships easier.† This is same circuit electrically |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Now it is obvious that the 8 Ω and the 16 Ω are in series
which becomes a 24 Ω
resistance which is in parallel with a 12 Ω
resistor.† SO the equivalent resistance
is |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
So |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
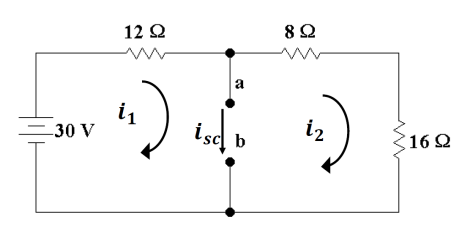
Now we have to find the short
circuit current between a and b |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
I have set up and labeled two
mesh currents.† The equations are |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
ans |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
The second equation gives |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
So our equivalent circuit can
be drawn as |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
So we can get i from current division |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|